148. [✔][M]排序链表
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
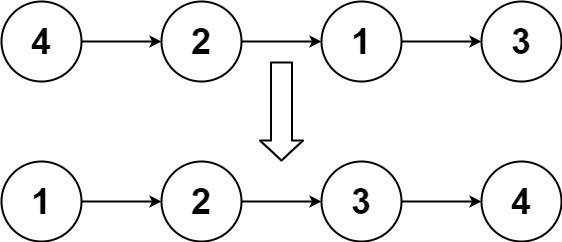
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例 2:

输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5 * 104]内 -105 <= Node.val <= 105
进阶: 你可以在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
题解:
核心点:归并排序
归并排序是先找到重点,讲数组一分为二,然后分别讲左半部分和右半部分不断的一份为二,对两部分进行排序,然后将部分最后合起来成为1个排序数组。
第一步是分:也就是找到重点一分为二
第二部分是和:将两个排序数组何为1个排序数组
// @lc code=start
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* val: number
* next: ListNode | null
* constructor(val?: number, next?: ListNode | null) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
* }
*/
function sortList(head: ListNode | null): ListNode | null {
if (head === null) {
return null
}
// 将首尾两个节点的链表不断拆分,然后调用合并函数合并为一条有序链表
const toSortList = (head: ListNode | null, tail: ListNode | null) => {
if (head === null) {
return
}
if (head.next === tail) {
head.next = null;
return head;
}
let slow = head;
let fast = head;
while (fast !== tail) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast !== tail) {
fast = fast.next;
}
}
let mid = slow;
return merge(toSortList(head, mid), toSortList(mid, tail));
}
// 将两个链表合并成1个有序链表
const merge = (head1: ListNode | null, head2: ListNode | null) => {
let dummy = new ListNode(0);
let temp = dummy, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2;
while (temp1 !== null && temp2 !== null) {
if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) {
temp.next = temp1;
temp1 = temp1.next;
} else {
temp.next = temp2;
temp2 = temp2.next;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp1 === null) {
temp.next = temp2;
}
if (temp2 === null) {
temp.next = temp1;
}
return dummy.next;
}
return toSortList(head, null);
};
// @lc code=end